Avoid security credentials on git public repository¶
AWS accounts, passwords and other sensitive information are a valuable target: outside attackers are continuously scraping GitHub for credentials embedded in the code.Security credential leaks expose sensitive data, resources utilization on your costs, or details of your infrastructure that could lead to sabotage. It is therefore essential to protect developers from releasing potentially harmful secrets on GitHub.
For our users, we strongly endorse the use of tools for automatic detection.
git-secrets¶
We found a helpful tool, preventing you from adding secrets to your Git repositories: git-secrets, which allows you to create hooks for your local repositories.
The tool causes a commit fails, for every commit containing (detected) security credentials. It requires configuration for each local repository that you want to protect.
It is possible to integrate its use in a CI system, detecting accidental commits, but this strategy will expose your secret.For this reason, we suggest to use it just as second layer protection (in the unfortunate case a developer forget to protect a local repository).
Installation¶
The following steps will download and install the latest version of git-secrets.
git clone https://github.com/awslabs/git-secrets
cd git-secrets
make install
Or, installing with Homebrew (for OS X users).
brew install git-secrets
Configuration¶
It is mandatory to install the git hooks for every repo that you wish to use with git secrets --install.
Here’s a quick example of how to ensure a git repository is scanned for secrets on each commit:
cd /path/to/repository
git secrets --install
git secrets --register-aws
Advanced configuration¶
First of all, have a look at the official /git-secrets repository.
Add a configuration template if you want to add hooks to all repositories you initialize or clone in the future.
git secrets --register-aws --global
Add hooks to all your local repositories.
git secrets --install ~/.git-templates/git-secrets
git config --global init.templateDir ~/.git-templates/git-secrets
Add custom providers to scan for security credentials.
git secrets --add-provider -- cat /path/to/secret/file/patterns
Before making public a repository¶
With git-secrets is also possible to scan a repository including all revisions:
git secrets --scan-history
Setting a Jenkins job guarding a repository¶
We suggest to set up a second layer protection with a CI task for detect accidental commits.
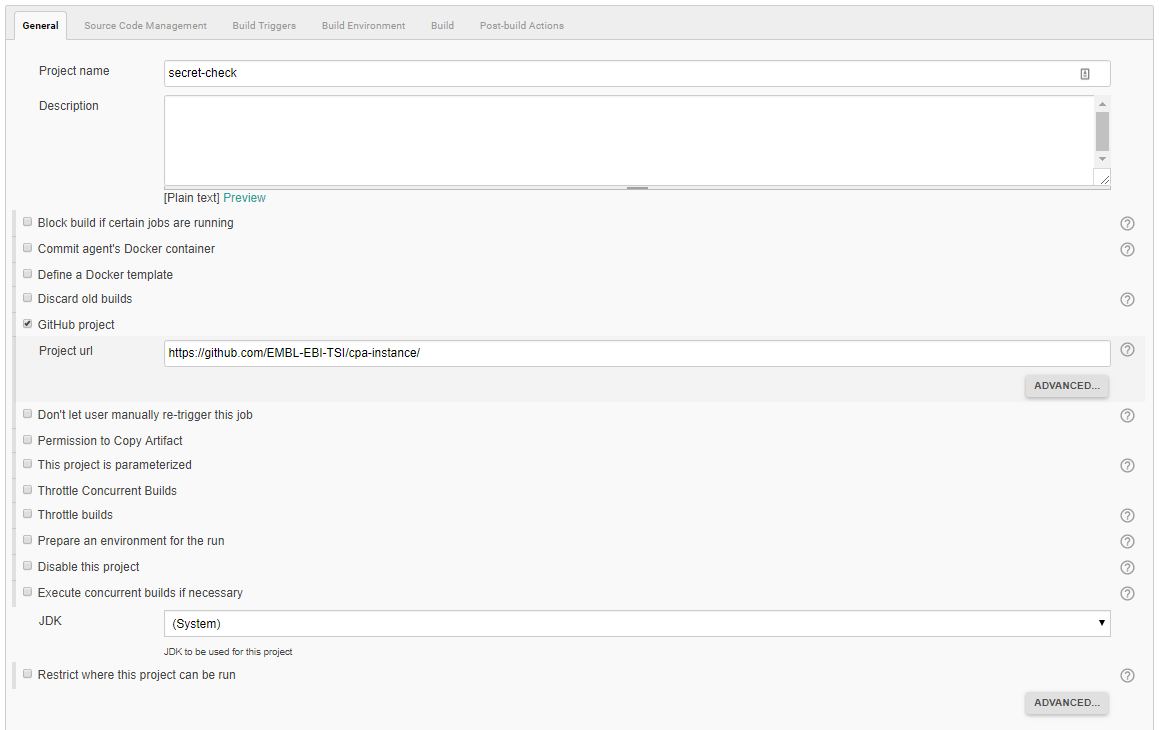
- Define a
GitHub project-Project url, underGenerali.e.:
https://github.com/EMBL-EBI-TSI/cpa-instance/
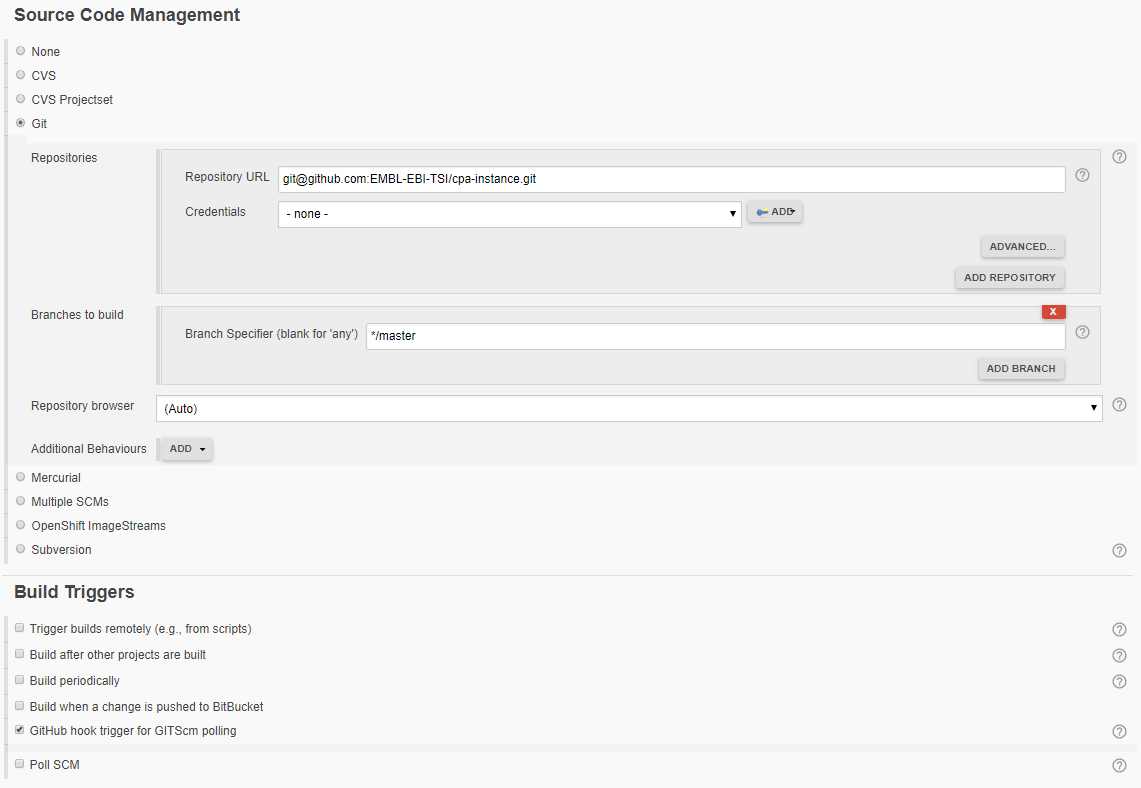
- Specify the same URL under:
Source Code Management-Git-Repositories-Repository URL - Flag
GitHub hook trigger for GITScm pollingunderBuild Triggers.
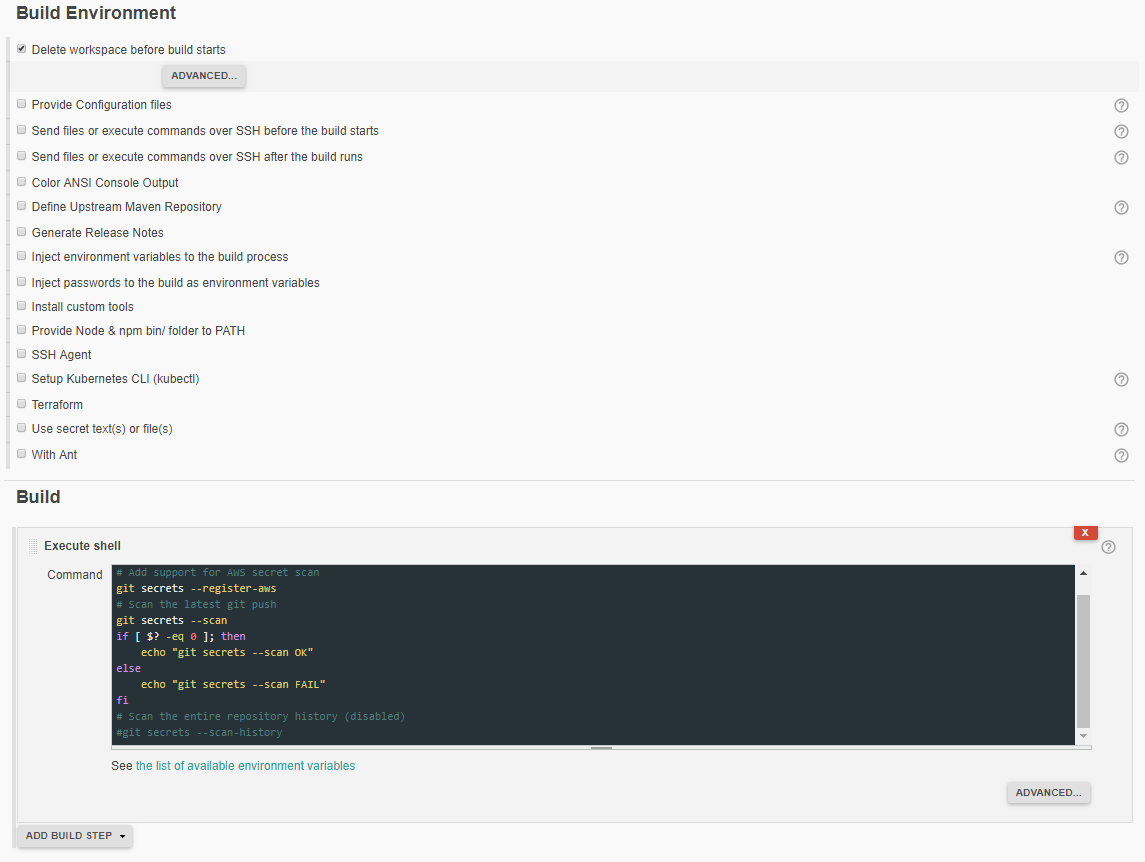
- Flag
Delete workspace before build startsunderBuild Environment. - Under
Build-Execute shell-Command
git secrets --install
# Add support for AWS secret scan
git secrets --register-aws
# Scan the latest git push
git secrets --scan
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "git secrets --scan OK"
else
echo "git secrets --scan FAIL"
For those with accounts on our jenkins server, this Jenkins job https://ci.tsi.ebi.ac.uk/job/app-testing/job/secret-check/ has the latest configuration and can be used as a template.